Monocytes
Definition, Absolute Ranges And Causes
Monocytes Definition
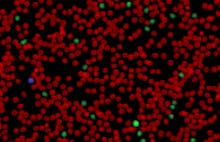
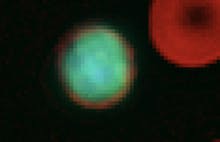
Monocytes are one of the largest types of white blood cells. Each type of white blood cell has a unique role. Monocytes are responsible for attacking and breaking down germs and bacteria that enter the body
Monocytes are phagocytic cells. This means they break down infections by “eating” them. They use their plasma membrane to engulf and break down dead cells or harmful foreign particles and bacteria.
Once they are a few hours old, monocytes travel through the bloodstream to organs and tissues such as the liver, lungs, spleen and bone marrow. When they get there, they stick onto the tissue and turn into a different type of cell: a macrophage.
These cells behave similarly to monocytes, but stay still on organs or tissues. They remove dead tissue, can kill cancer cells, and regulate the body’s immunity against foreign substances.
Some monocytes don’t turn into macrophages but instead become dendritic cells. These are responsible for working with T lymphocytes, often called T-cells. The dendritic cells present leftover debris from broken down cells, viruses, bacteria and other foreign substances to the T-cells. This information helps the T-cells form a plan for fighting the invader.
What is absolute monocytes count and how is it measured?
An absolute blood cell count is a part of the results of a blood test. It is when the number of cells is expressed as an absolute number, rather than as a percentage.
The absolute monocytes count can be worked out by multiplying the total number of white blood cells in the body against the percentage of white blood cells which are monocytes. For example, if the white blood cell count is 8000, and 5% of those white blood cells are monocytes, then the absolute count of monocytes would be 400 (8000 x 0.05).
What is the normal range for monocytes?
Monocytes make up around 1 to 10% of the circulating white blood cells, although for most people it is closer to between 2 and 8%. Men usually have a slightly higher count of monocytes than women.
The normal absolute monocytes range is between 1 and 10% of the body’s white blood cells. If the body has 8000 white blood cells, then the normal absolute monocytes range is between 80 and 800.
Having an absolute monocytes count that is higher or lower than typical is not dangerous in itself, but it can indicate that the person needs to be examined further. The absolute monocytes count can be a valuable way to evaluate the overall health of the body’s immune system.
What causes high monocytes count?
A high monocyte count or high monocyte can indicate other medical conditions. An infection by a bacteria, virus or fungus can cause an increase in monocyte levels. This is because the body creates more monocytes to fight the invader. An absolute monocytes high can also be a response to stress, chronic infections or autoimmune disorders.
Sometimes, a count outside of the normal absolute monocytes range may suggest that there is a problem with the way the body produces new blood cells. This can indicate certain types of blood conditions.
In rare cases, the high count may be due to a malignant growth, such as leukemia.
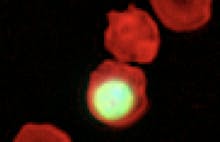
Differences between monocytes and macrophages
Macrophages are monocytes that have finished their tasks in the bloodstream, and have moved to other organs or tissues in the body and matured.
The two types of cell are similar: both monocytes and macrophages are both responsible for destroying harmful substances. The key differences are that macrophages are about double the size of monocytes. Macrophages stay stationary in extracellular fluid, but monocytes move through the bloodstream.
Discover Sight OLO - Automated Hematology Analyzer
Disclaimer: The content of this knowledge post intends to provide general information related to topics that are relevant to blood diagnostics and may not be used in relation to the operation of Sight OLO. For detailed information on the diagnostic parameters and specifications of Sight OLO, please refer to the official Operator's Manual.